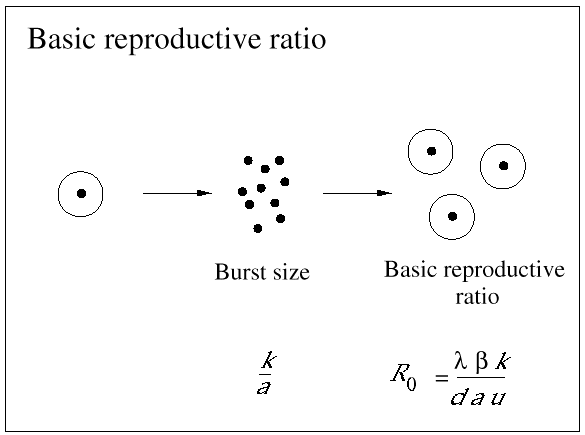
Fig. 2.The basic reproductive ratio, R0, of a virus infection is defined as the number of secondary infected cells that arise out of any one infected cell at the beginning of the infection, when the supply of uninfected cells is not limited. In terms of the basic model of virus dynamics, the average number of free virus particles that are generated by a single infected cell (the so-called ''burst size'') is k/a, whereas the basic reproductive ratio is given by
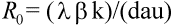 (4)
(4)
If R0 > 1, then a ''chain reaction'' will generate an explosive increase in virus abundance at the beginning of infection. If R0 < 1 (for example, as a consequence of vaccination), then the individual is protected against infection.
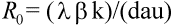 (4)
(4)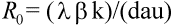 (4)
(4)